The sheet metal trade offers a stable and well-compensated career path in Boston, MA, with opportunities for professional growth, union membership, and exposure to innovative technologies in the field. As of 2025, Boston maintains around 31 job openings in the sheet metal sector, while wages range from $18–$64 per hour, reflecting a diversity of roles from entry-level to skilled positions [source 7][source 9][source 10]. To begin a career in this trade, prospective workers must first apply for a state-approved apprenticeship—a five-year program encompassing 2,000 hours of on-the-job training annually and 200 hours of classroom instruction [source 2][source 5]. This pathway leads to a journeyperson license, which is required to perform independent sheet metal work. Entry into the trade is supported by institutions like Sheet Metal Workers Local 17 JATC, which oversees a joint apprenticeship program with the Sheet Metal & Air Conditioning Association of Boston [source 7]. Interested individuals can explore current apprenticeships and job listings through platforms like Gild [source 1], ensuring access to structured training and employment opportunities, while for additional salary insights, check Indeed [source 9]. Beyond Boston, salaries remain competitive, aligning well with or slightly surpassing the national average of $51,990 annually or roughly $25 hourly [source 10], supported by wage agreements in place through 2026 [source 8].
Before pursuing formal training, it's essential to understand what a career in sheet metal entails. Sheet metal workers fabricate, install, and maintain products made of thin metal sheets, including ductwork, flashing, gutters, roofing, and other components used in HVAC systems and construction, as detailed in resources like Boston Metal's advancements [source 10]. Their work supports both residential and commercial building sectors, often requiring specialized skills in blueprint reading, welding, and tool use. As Boston continues to develop its infrastructure and focus on sustainability, the sheet metal industry remains a foundational trade with evolving opportunities in automated fabrication and green manufacturing practices [source 10].


Yes. Massachusetts mandates that all sheet metal workers must be licensed at either the apprentice or journeyperson level to perform trade-specific activities legally [source 1]. To begin work in the field, individuals must secure employment under a master licensee and apply for a Massachusetts Apprentice Sheet Metal Worker License [source 10]. Upon completion of the apprenticeship, workers pursue their Journeyperson license. There are two classifications:
Obtaining the license involves submitting documents such as a high school diploma or GED, work experience verification, apprentice license records, and a current photo for identification purposes. For more on licensing processes, review Local 17's site [source 9].

To qualify for a sheet metal apprenticeship in Boston, individuals must:
The primary apprenticeship program in the region is administered by Sheet Metal Workers Local 17 Joint Apprenticeship Training Committee (JATC) in partnership with contractors. The application process is competitive and includes:
The apprenticeship lasts five years, with structured progression through classroom and on-the-job instruction [source 2]. Additionally, for job search support, explore ZipRecruiter [source 10].
| Year | Core Training Areas | Technical Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Year 1 | OSHA 30 safety, layout, math, tool use, CPR/first aid | 150 hours |
| Year 2 | Advanced math, blueprint reading, welding | 150 hours |
| Years 3-5 | Fabrication, field measurements, fire damper systems, specialized tools and safety | 150 hours annually |
Apprentices earn wages during their training, gaining progressively advanced responsibilities as they proceed through the program.
Upon completing the apprenticeship and obtaining a journeyperson license, individuals can join Sheet Metal Workers Local 17, gaining access to:
Union membership enhances job security and ensures quality representation in the trade workforce. Prospective apprentices can reach out to John Healy, the Program Director at jhealy@lu17jatc.org or call 617-298-0850 for detailed instructions and training information [source 5].
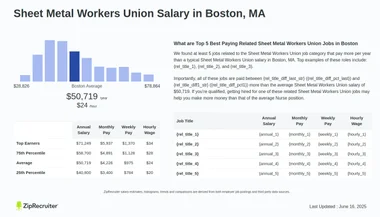
Sheet metal workers in Boston earn a competitive wage, with the average starting wage at $18 per hour, and experienced workers making upward of $35–$38 per hour on platforms like ZipRecruiter and Indeed [source 6][source 9]. Union contracts in Boston ensure stable wage increases through at least 2026, enhancing long-term earning potential [source 8]. For detailed salary comparisons, visit Indeed's page [source 9].
While national employment growth is projected at 2% from 2023–2033, Boston is witnessing unique opportunities in sustainable metals production, led by companies like Boston Metal, a company advancing decarbonized steelmaking through innovative electrolysis-based technology [source 10]. This positions Boston as a potential hub for high-tech sheet metal manufacturing and construction integration.
Workers seeking advancement can focus on areas like:
With targeted continuing education and certifications in these fields, sheet metal professionals can build lucrative long-term careers in Boston's evolving trade landscape.
While the primary training pathway is through Local 17 JATC, Boston also offers related educational options:
These programs help complement hands-on apprenticeship work with academic grounding and prepare candidates for industry certifications and licensing exams.
Sheet metal work poses physical demands, such as manual labor, working at heights, and operating power tools. To mitigate job-related injuries and ensure consistent work quality, Boston adheres to strict safety regulations, including OSHA certifications and trade-specific licensing. Apprentices are required to complete OSHA 30-hour training during their first year [source 2]. Technological changes like automated fabrication and building information modeling (BIM) integration require workers to pursue ongoing skill development through the Local 17 apprenticeship curriculum and industry training forums [source 7]. For visual guidance on industry practices, check this video [source 2]. By staying current with these trends, sheet metal workers can secure long-term relevance in a progressively digital construction environment.
If you're ready to begin a debt-free, high-demand career in Boston, sheet metal offers a valuable entry point into the skilled trades. Apprenticeships are structured to ensure steady income growth, benefits access, and union protections, giving new workers a clear career roadmap. The first step is applying for the apprenticeship through Sheet Metal Workers Local 17 and positioning yourself for a competitive interview and job offer. You can also use platforms like Gild [source 1] to explore available apprenticeships in real time and start building a future in the trade. With a strong demand for HVAC, building infrastructure, and sustainable metal production, 2025 presents an excellent opportunity to begin your sheet metal career journey—right in Boston.

